Welcome to our comprehensive guide on biochemistry, the branch of science that studies the chemical processes and substances within living organisms.
This guide will cover the fundamental concepts, structures, and functions of biochemistry, as well as some of the latest developments and applications in the field.
We aim to provide you with a rich and detailed overview of biochemistry that can help you understand and appreciate the wonders of life.
What is Biochemistry?
Biochemistry is the study of the chemical basis of life. It involves investigating the molecular and cellular processes that underlie the properties and behaviors of living systems, from the smallest bacteria to the largest mammals.
Biochemistry combines the principles and techniques of chemistry, physics, biology, and mathematics to unravel the complexity of life at the molecular level.
The Structure of Biomolecules
The building blocks of life are molecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids, that are made up of atoms and arranged in specific ways.
These molecules have different structures and properties that allow them to perform various functions in cells and tissues. For example, proteins are the workhorses of the cell, catalyzing reactions, transporting molecules, and providing structural support.
Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, contain the genetic information that controls the synthesis and function of proteins. Carbohydrates and lipids are energy sources, storage molecules, and structural components of cell membranes and other tissues.
The Function of Biomolecules
The functions of biomolecules depend on their structure, which is determined by their sequence and interactions with other molecules.
- Proteins, for example, can fold into specific shapes that enable them to interact with other molecules in precise ways.
- Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction.
- Hormones are signaling molecules that regulate physiological processes by binding to specific cell receptors.
- DNA and RNA are involved in the replication, transcription, and translation of genetic information.
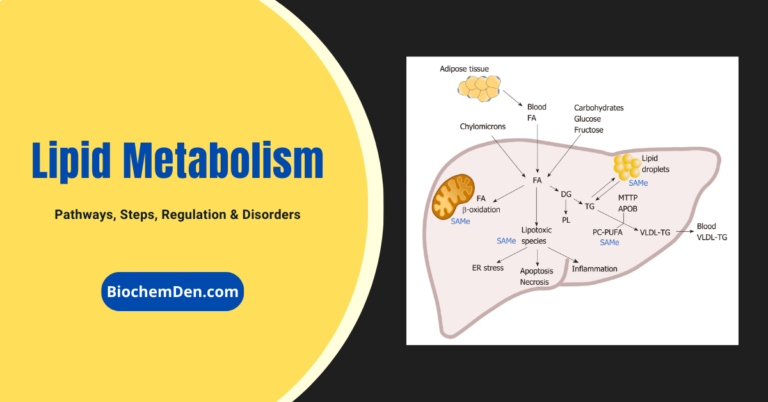
Biochemical Pathways and Metabolism
Biochemical pathways are sequences of reactions that convert one molecule into another, often with the help of enzymes and cofactors.
These pathways are interconnected and regulated to ensure the proper balance and flow of metabolites in cells and tissues.
Metabolism is the collective term for all the biochemical reactions that occur in an organism, including the synthesis and breakdown of biomolecules and the production and consumption of energy.
Metabolism can be divided into catabolism, which breaks down molecules and releases energy, and anabolism, which synthesizes molecules and requires energy.
Applications of Biochemistry
- Biochemistry has many practical applications in medicine, industry, agriculture, and environmental science. For example, biochemistry is essential for understanding the mechanisms of diseases and developing new drugs and therapies.
- It is also used in biotechnology to produce recombinant proteins, genetically modified organisms, and vaccines.
- In agriculture, biochemistry is involved in producing fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically modified crops.
- In environmental science, biochemistry is used to study the effects of pollutants and toxins on living systems.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide on biochemistry, we have covered the fundamental concepts, structures, and functions of biochemistry, as well as some of the latest developments and applications in the field.
We hope this guide has helped you gain a deeper understanding and appreciation of the wonders of life. If you have any questions or feedback, don’t hesitate to get in touch with us. Thank you for reading.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the significant biomolecules studied in biochemistry?
The major biomolecules studied in biochemistry are proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. These molecules have different structures and functions that allow them to perform various activities in cells and tissues.
What is the structure of proteins?
Proteins are large, complex molecules made up of amino acid units linked together by peptide bonds. Proteins have a primary structure (sequence of amino acids), a secondary structure (alpha helices and beta sheets), a tertiary structure (three-dimensional shape), and a quaternary structure (combination of multiple protein subunits).
What is the role of enzymes in biochemical reactions?
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. Enzymes bind to specific substrates and convert them into products through chemical steps. Enzymes are particular and can catalyze reactions at remarkable rates.
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
The central dogma of molecular biology is the flow of genetic information from DNA to RNA to protein. DNA serves as the genetic blueprint for synthesizing RNA, which in turn directs the production of proteins. This flow of information is essential for the proper function of living systems.
What is metabolism?
Metabolism is the collective term for all the biochemical reactions that occur in an organism. It involves the synthesis and breakdown of biomolecules and the production and consumption of energy. Metabolism can be divided into catabolism, which breaks down molecules and releases energy, and anabolism, which synthesizes molecules and requires energy.