What is the Nobel Prize, and who is Alfred Nobel? Since 1901, the Nobel Prize has been honoring men and women from all corners of the globe for outstanding achievements in physics, chemistry, physiology or medicine, literature, and work for peace. Here is the list of Nobel Prizes in Physiology or Medicine below, from 2001 to 2024.
The foundations for the prize were laid in 1895, when Alfred Nobel wrote his last will, leaving much of his wealth to the establishment of the Nobel Award. But who was Alfred Nobel?

They present here articles, photographs, a slide show, and poetry written by Nobel to give a glimpse of a man whose varied interests in the prize he established.
Nobel Prize in Physiology (or) Medicine List
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2024

The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun for discovering microRNA (miRNA) and its role in gene regulation. Their work revealed how small RNA molecules, like lin-4 in roundworms, control gene expression by silencing specific messenger RNAs (mRNAs) after transcription. This discovery showed that miRNAs are a universal mechanism in plants, animals, and humans, influencing development, immunity, and diseases like cancer.
Their findings revolutionized molecular biology, leading to new diagnostic tools and treatments, such as miRNA-based biomarkers and RNA-targeting drugs. By uncovering this hidden layer of gene control, Ambros and Ruvkun transformed our understanding of genetics and opened new paths for medical research and therapy. Their work is a landmark achievement with profound impacts on science and medicine.
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2023

The 2023 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine went to Katalin Karikó and Drew Weissman for their work on mRNA vaccines. Their research made it possible to quickly develop effective mRNA vaccines against COVID-19. By modifying mRNA molecules, they created the foundation for this technology, which played a crucial role in fighting the pandemic. Their contributions saved countless lives and marked a major advancement in vaccine development.
Nobel prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2022

The 2022 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded to Svante Pääbo for his groundbreaking work in decoding the DNA of ancient human relatives like Neanderthals and Denisovans. His research revealed how these extinct species interbred with modern humans, offering new insights into human evolution. Pääbo’s discoveries in sequencing ancient DNA created the field of paleogenomics, transforming our understanding of human origins and migration from Africa.
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2021

Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2020

Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2019
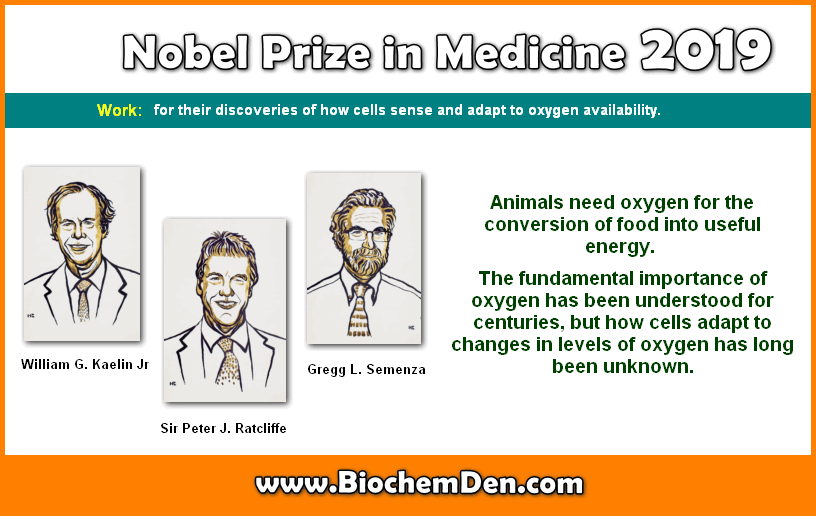
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2019 was awarded jointly to William G. Kaelin Jr, Sir Peter J. Ratcliffe, and Gregg L. Semenza “for their discoveries of how cells sense and adapt to oxygen availability.”
Nobel Prize In Physiology or Medicine in 2018
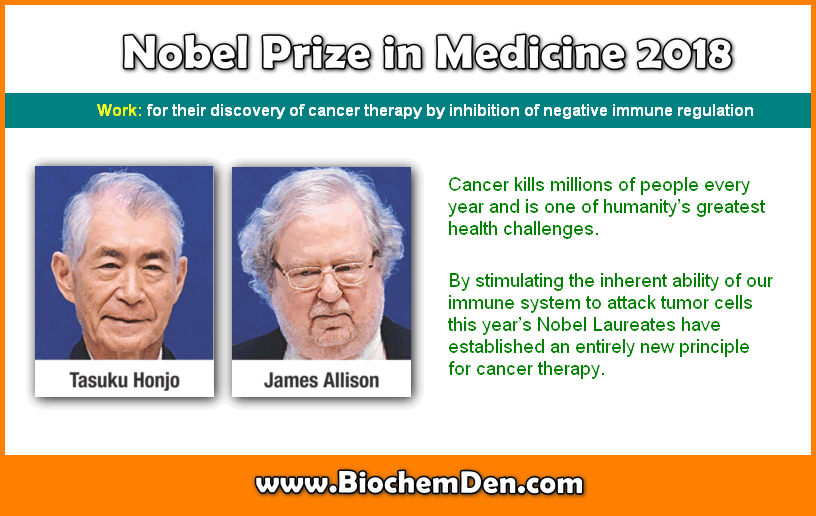
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2018 was awarded jointly to Tasuku Honjo, and James Allison. Cancer kills millions of people every year and is one of humanity’s greatest health challenges. By stimulating the inherent ability of our immune system to attack tumor cells this year’s Nobel laureates have established an entirely new principle for cancer therapy.
Nobel Prize In Physiology or Medicine in 2017

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2017 was awarded jointly to Jeffrey C. Hall, Michael Rosbash and Michael W. Young “for their discoveries of molecular mechanisms controlling the circadian rhythm“.
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2016

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2016 was awarded to Yoshinori Ohsumi “for his discoveries of mechanisms for autophagy“.
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2015

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2015 was divided, one half jointly to William C. Campbell and Satoshi Ōmura “for their discoveries concerning a novel therapy against infections caused by roundworm parasites“ and the other half to Youyou Tu “for her discoveries concerning a novel therapy against Malaria“.
Nobel Prize In Physiology or Medicine in 2014

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2014 was divided into two halves, with one half awarded to John O Keefe, the other half jointly to May-Britt Moser and Edvard I. Moser “for their discoveries of cells that constitute a positioning system in the brain“.
Nobel Prize In Physiology or Medicine in 2013

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2013 was awarded jointly to James E. Rothman, Randy W. Schekman and Thomas C. Südhof “for their discoveries of machinery regulating vesicle traffic, a major transport system in our cells“.
Nobel Prize In Physiology or Medicine in 2012
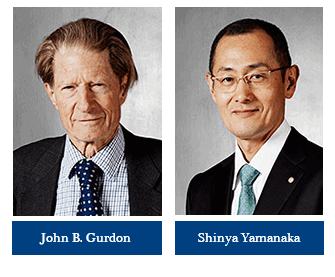
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2012 was awarded jointly to Sir John B. Gurdon and Shinya Yamanaka “for the discovery that mature cells can be reprogrammed to become pluripotent”
Nobel Prize In Physiology or Medicine in 2011
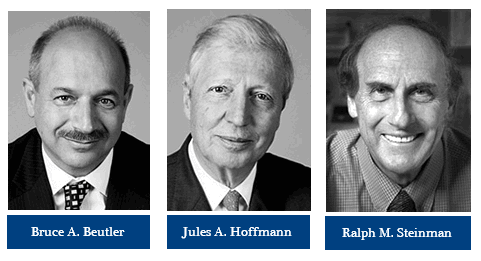
The Nobel Prize in Medicine 2011 was divided, one half jointly to Bruce A. Beutler and Jules A. Hoffmann “for their discoveries concerning the activation of innate immunity“ and the other half to Ralph M. Steinman “for his discovery of the dendritic cell and its role in adaptive immunity“.
Nobel Prize In Physiology or Medicine in 2010

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2010 was awarded to Robert G. Edwards “for the development of in vitro fertilization“.
Nobel Prize In Physiology or Medicine in 2009
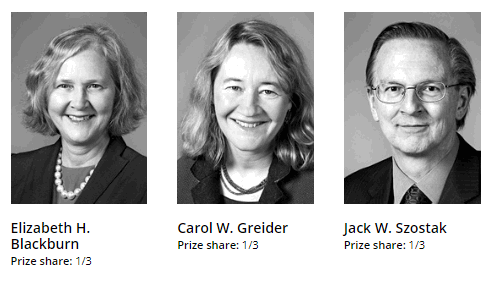
The Nobel Prize in Physiology 2009 was awarded jointly to Elizabeth H. Blackburn, Carol W. Greider and Jack W. Szostak “for the discovery of how chromosomes are protected by telomeres and the enzyme telomerase“.
Nobel Prize In Nobel prize in Chemistry 2009
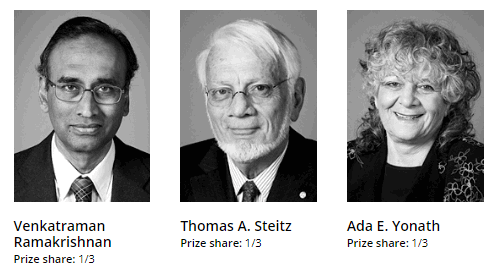
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2009 was awarded jointly to Venkatraman Ramakrishnan, Thomas A. Steitz, and Ada E. Yonath “for studies of the structure and function of the ribosome“.
Nobel Prize In Physiology or Medicine in 2008
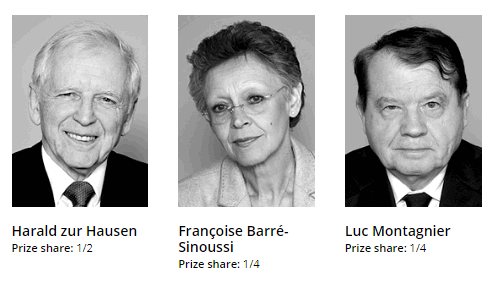
The Nobel Prize in Medicine 2008 was divided into two halves, with one half awarded to Harald Zur Hausen “for his discovery of human papilloma viruses causing cervical cancer“, the other half jointly to Françoise Barré-Sinoussi and Luc Montagnier “for their discovery of human immunodeficiency virus“.
Nobel Prize In Physiology or Medicine in 2007

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2007 was awarded jointly to Mario R. Capecchi, Sir Martin J. Evans and Oliver Smithies “for their discoveries of principles for introducing specific gene modifications in mice by the use of embryonic stem cells“.
Nobel Prize In Physiology or Medicine in 2006

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2006 was awarded jointly to Andrew Z. Fire and Craig C. Mello “for their discovery of RNA interference – gene silencing by double-stranded RNA.“
Nobel Prize In Physiology or Medicine in 2005

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2005 was awarded jointly to Barry J. Marshall and J. Robin Warren “for their discovery of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastritis and peptic ulcer disease”
Nobel Prize In Physiology or Medicine in 2004

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2004 was awarded jointly to Richard Axel and Linda B. Buck “for their discoveries of odorant receptors and the organization of the olfactory system“
Nobel Prize In Physiology or Medicine in 2003

The Nobel Prize in Medicine 2003 was awarded jointly to Paul C. Lauterbur and Sir Peter Mansfield “for their discoveries concerning magnetic resonance imaging“.
Nobel Prize In Physiology or Medicine in 2002
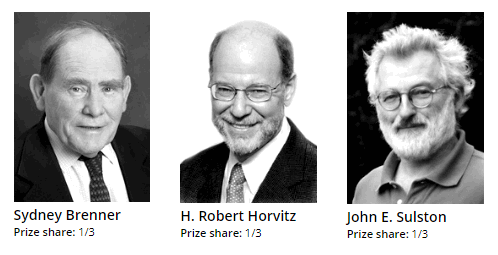
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2002 was awarded jointly to Sydney Brenner, H. Robert Horvitz, and John E. Sulston “for their di, coveries concerning genetic regulation of organ development and programmed cell death“.
Nobel Prize In Physiology or Medicine in 2001
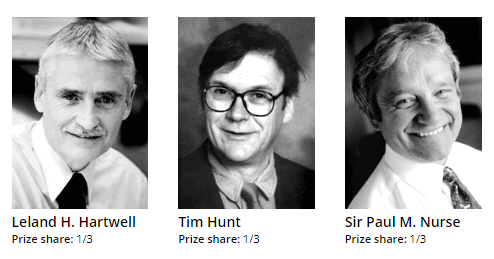
The Nobel Prize in Medicine 2001 was awarded jointly to Leland H. Hartwell, Tim Hunt, and Sir Paul M. Nurse “for their discoveries of key regulators of the cell cycle“.
Reference: List of Nobel Prizes in Medicine and Physiology
Discover more from Biochemistry Den
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

