Are you interested to know what the condition of Blood Sugar after a Meal is? Blood sugar, or glucose, is a crucial component of our body’s energy system. It is the primary source of fuel for the cells that make up our body, including the brain. However, the level of blood sugar can be affected by the food we eat and how our body processes it.
Understanding what happens to blood sugar after a meal is essential for people with diabetes, but it’s also important for anyone who wants to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
It is usually an increase in blood sugar after a meal because many foods contain glucose. More sugar or carbohydrate content of food causes blood sugar levels to rise. Some foods, such as refined carbohydrates, cause a sudden and slow rise in blood sugar.
Others, such as those high in fiber, increase more gradually. The best way for an individual to test their blood sugar after a meal to determine the exact amount is to use portable blood glucose meters. which is a small device that measures blood sugar levels using thin strips and a blood sample.
They are most commonly used by diabetics to control blood sugar levels and ensure that they are not too high or too low, but many people can benefit from keeping an eye on their blood sugar levels throughout the day.
What happens to Blood Sugar after a Meal?
After we eat, our body begins to digest the food and break it down into its component parts. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. As the glucose enters the bloodstream, the pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps the cells in the body absorb the glucose and use it for energy. This process helps to keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
If we eat a meal that is high in carbohydrates or sugar, our body will produce more insulin to manage the increased amount of glucose in the bloodstream. However, if our body is not producing enough insulin or is unable to use it effectively, blood sugar levels can become too high, leading to hyperglycemia.
On the other hand, if we eat a low-carbohydrate meal or one that is high in protein and fat, our body will produce less insulin, and blood sugar levels may remain stable or even decrease slightly. This is because proteins and fats are broken down more slowly than carbohydrates, so the glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream more gradually.
The Digestion Process
When we eat, our digestive system breaks down the food into its component parts, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which is absorbed into the bloodstream through the small intestine.
The Role of Insulin
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps the cells in the body absorb glucose and use it for energy. After a meal, the pancreas releases insulin into the bloodstream to help manage the increased level of glucose.
The Impact of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the primary source of glucose in our diet. If we eat a meal that is high in carbohydrates, our body will produce more insulin to manage the increased level of glucose in the bloodstream.
The Effect of Protein and Fat
Proteins and fats are broken down more slowly than carbohydrates, so the glucose is absorbed into the bloodstream more gradually. This means that a meal that is high in protein and fat may not cause as much of an increase in blood sugar levels.
Simple vs. Complex Carbohydrates
Not all carbohydrates are created equal. Simple carbohydrates, such as sugar, are broken down quickly and can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains and vegetables, are broken down more slowly and can help to maintain more stable blood sugar levels.
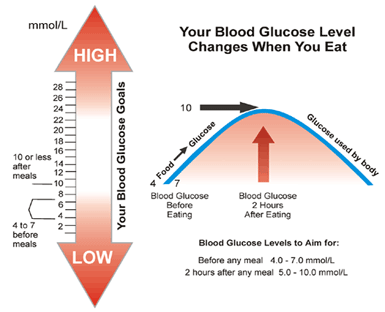
Glycemic Index
The glycemic index is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a high glycemic index, such as white bread and sugary drinks, can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels, while foods with a low glycemic index, such as whole grains and fruits, are absorbed more slowly.
Anyone who is concerned about their blood sugar levels should talk to their physician. Both forms of diabetes can be treated. Type 2 diabetes can often be prevented and even managed with some dietary changes.
Sugar in the blood normally varies throughout the day and is usually at its lowest level since the morning before breakfast.
Frequently Answers Questions (FAQs)
What is the normal range for blood sugar levels?
For most people, a normal range for blood sugar levels is between 70 and 140 mg/dL. However, this range may vary depending on various factors, such as age, weight, and overall health. Blood sugar levels are typically lower in the morning after fasting overnight and can increase after a meal, but they should still fall within a normal range.
How long does it take for blood sugar levels to return to normal after a meal?
How long does it take for blood sugar levels to return to normal after a meal?
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
Symptoms of high blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, may include increased thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, fatigue, and headaches.
How can I manage my blood sugar levels after a meal?
Eating a balanced meal that includes a variety of healthy carbohydrates, proteins, and fats can help to manage blood sugar levels. Regular exercise can also help to regulate blood sugar levels by improving insulin sensitivity.
Can certain foods affect blood sugar levels more than others?
Yes, certain foods can cause a more significant increase in blood sugar levels than others. Foods that are high in carbohydrates, such as bread, pasta, and sugary snacks, can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels. Foods that are high in fiber and protein, such as vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, can help to slow the absorption of carbohydrates and prevent a sudden spike in blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
Understanding what happens to blood sugar after a meal is crucial for managing diabetes and maintaining overall health.
By eating a balanced meal that includes a variety of healthy carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, and regularly exercising, we can help to keep our blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
By following these simple steps, we can take control of our health and enjoy a happier, healthier life.
Discover more from Biochemistry Den
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.