The assay of salivary amylase enzyme activity is a non-invasive, cost-effective, and reliable method for measuring the amount of amylase in human saliva.
Amylase is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the digestion of carbohydrates, breaking them down into smaller sugars that the body can absorb.
The amount of amylase in saliva can vary depending on various factors such as diet, stress, and certain medical conditions.

The assay of salivary amylase activity can provide valuable information about the efficiency of the digestive system, the response to stress, and the presence of metabolic disorders.
This article will discuss the importance and methodology of the assay of salivary amylase enzyme activity.
Salivary amylase is an enzyme produced by the salivary glands. Formerly known as ptyalin, it breaks down starch into maltose and isomaltose. Amylase, like other enzymes, works as a catalyst. This protocol is the basic laboratory procedure for the assay of salivary amylase activity.
All catalysts are enzymes, but not all enzymes are catalysts. A catalyst is a substance that hastens a chemical reaction but does not become part of the end product.
What is Amylase?
Amylase is an enzyme responsible for breaking down carbohydrates, it is found in saliva and pancreatic juice, and it helps the body digest food. Amylase is also used in brewing and baking, as it helps convert starch into sugar.
What is the salivary amylase structure?
Salivary amylase, also known as ptyalin, is an enzyme in the saliva responsible for breaking down complex carbohydrates into simpler sugars.
Its structure comprises a single polypeptide chain with a molecular weight of approximately 56 kDa. Salivary amylase is a globular protein, meaning that it has a three-dimensional shape that is folded into a compact structure.
Its active site, where the carbohydrate substrate binds and undergoes hydrolysis, is located in an aperture on the protein’s surface.
The structure of salivary amylase is critical to its function in the digestive process, as it allows for the efficient hydrolysis of carbohydrates in the mouth before they enter the stomach and small intestine for further digestion and absorption.
An enzyme is a protein molecule that is a biological catalyst with three characteristics.
- The basic function of an enzyme is to increase the rate of a reaction.
- Most enzymes act specifically with only one reactant, called a substrate, to produce products.
- The most remarkable characteristic is that enzymes are regulated from a state of low activity to high activity and vice versa.
The activity of enzymes is strongly affected by changes in pH and temperature. Each enzyme works best at a certain pH and temperature, with its activity decreasing at values above and below that point due to denaturation.
For enzymes, denaturation can be defined as the loss of enough structure, rendering the enzyme inactive. This is not surprising, considering the importance of tertiary structure in enzyme function and non-covalent forces in determining the shape of enzymes.
Basic Classification of Amylase
Amylase is a type of enzyme that is responsible for breaking down carbohydrates into simpler sugars.
It can be classified into three main categories based on their origin and properties:
- Alpha-amylase: This type of amylase is found in many organisms, including humans, and is involved in the breakdown of starch and glycogen into simple sugars such as glucose, maltose, and maltotriose.
- Beta-amylase: This type of amylase is found primarily in plants and is involved in breaking starch and other complex carbohydrates into maltose and other disaccharides.
- Gamma-amylase: This type of amylase is found in certain bacteria and fungi and is involved in breaking complex carbohydrates into glucose and maltose.
Each type of amylase has a specific substrate and catalytic mechanism, and its activity can be influenced by factors such as temperature, pH, and the presence of other compounds.
Understanding the basic classification of amylase is important in various fields, such as food science and biotechnology, as it can optimize enzymatic reactions and develop new applications for these enzymes.
What are the functions of salivary amylase?
Salivary amylase, also known as ptyalin, is an enzyme found in the saliva that plays an important role in the digestion of carbohydrates. The functions of salivary amylase include:
- Breakdown of complex carbohydrates: Salivary amylase catalyses the hydrolysis of complex carbohydrates, such as starch and glycogen, into simpler sugars like maltose and glucose.
- Initiation of digestion: Salivary amylase begins the process of carbohydrate digestion in the mouth before the food enters the stomach and small intestine.
- Improved taste: Salivary amylase can enhance the perception of sweetness in foods by breaking down complex carbohydrates into simpler sugars.
- Anti-bacterial properties: Salivary amylase also exhibits some anti-bacterial properties and can inhibit the growth of certain harmful bacteria in the mouth.
- Buffering action: Salivary amylase can help maintain the mouth’s pH balance by acting as a buffer against acidic compounds.
Overall, salivary amylase plays a crucial role in the digestion of carbohydrates and in maintaining oral health.
This article providing information on “Salivary amylase, functions, and Assay of Salivary amylase activity”.
Assay of Salivary Amylase activity
Aim
To determine activity of Amylase enzyme in Saliva
Principle
Amylase is the hydrolytic enzyme that breaks down many polysaccharides like starch, amylose, and dextrin and yields a disaccharide, i.e., maltose.
(C6H10O5)n + H2O → n(C12 H22 O11)
Reagents
- Substrate (Starch): Mix 1 gm of soluble starch in 200ml of 0.1M Phosphate buffer (pH 6.8) boil for 3 minutes and cool to room temperature and filter it necessary.
- Enzyme: Saliva is the best and easily available source of amylase. Collect some saliva in a beaker and dilute it to 1:20 dilution with distilled water.
- 1% Sodium chloride: It is necessary for enzyme activity
- DNS (Dinitro Salicylic acid): Dissolve 1.6 gm of NaOH in 20ml of distilled water. Take 1gm of 3,5 DNS in NaOH solution. In other beaker take 30gm of Sodium potassium tartrate. Dissolve in 50ml of distilled water. Mix this DNS solution and finally make the volume up to 100ml with distilled water.
- Standard solution of Maltose: It is prepared by dissolving 200mg Maltose in 100ml of water (2mg / 1ml).
Procedure
- Take 0.5ml of substrate and 0.2ml of 1% NaCl in a test tube and pre-incubated at 370C for 10 minutes then add 0.3ml of diluted saliva and incubate for 15 minutes at 370C.
- Stop the reaction by addition of 1 ml of DNS reagent mix well and keep the test tubes in a boiling water bath for 10 minutes.
- Cool and dilute with 10ml of distilled water.
- Read the color developed at 520 nm. Simultaneously setup the color developed at 520nm.
- Simultaneously setup the blank as per the test by adding DNS prior to the addition of enzyme simultaneously.
- Set up the standards of different test tubes and repeat the experiment as per the test and measure the color developed at 520nm absorbance.
Preparation of phosphate buffer
- Dissolve 0.2M (2.7218 grams) of KH2PO4 in 100ml of distilled water to this solution add 0.5M (2.8053 grams) KOH drop by drop till the pH is set to 6.8.
- Then make it to 200ml with distilled water. So, the final concentration is 0.1M of 200ml Phosphate buffer.
Result
The amount of Maltose in the given unknown sample is _________ grams of Maltose formed per 100ml of enzyme per one hour.
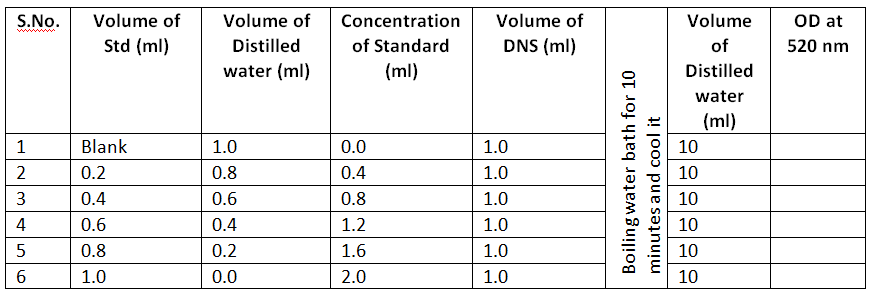
Calculation
- 1.5 mg of Maltose formed / 0.3. ml / 15 minutes.
- 1.5 X 4 mg of Maltose formed / 0.3 ml of Enzyme / 1 hour.
- 1.5 X 4 X 3.3 mg of Maltose formed / 1ml of Enzyme / 1 hour
- 1.5 X 4 X 3.3 X 100 mg of Maltose formed / 100ml of Enzyme / 1 hour
- Estimation of Carbohydrates by the Anthrone Method
- Assay of Acid Phosphatase enzyme activity from Potatoes
- Assay of Urease Enzyme Activity (Enzymology Practical Protocol)
- Effect of Temperature on Amylase activity (Enzymology Protocol)
- Assay of Salivary Amylase enzyme activity
Get this protocol in PDF format. Just download this “Determination of Salivary Amylase Activity” file, print it, and distribute it to the students. It helps you protect your students from spelling mistakes and volumetric errors. All the best
Importance of Assay of Salivary amylase enzyme
Assaying of salivary amylase enzyme is an important tool to understand the level of enzyme activity in saliva. Some of the key reasons why salivary amylase assay is important to include:
- Monitoring oral health: Salivary amylase assay can help monitor the oral cavity’s health and identify any potential oral health issues, such as periodontal disease or oral cancer.
- Studying digestive function: Salivary amylase assay is used to study the digestive system’s function and determine how efficiently the body is breaking down carbohydrates.
- Identifying metabolic disorders: Abnormal levels of salivary amylase activity can indicate underlying metabolic disorders, such as diabetes or pancreatitis.
- Nutritional analysis: Salivary amylase assay can determine nutritional deficiencies and imbalances in the body.
- Studying stress response: Salivary amylase activity can also be used as a non-invasive biomarker to study the physiological stress response.
Overall, the assay of salivary amylase enzyme is an important tool for researching, diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions.
Final words
Determining salivary amylase activity is an important tool for understanding various health conditions. The activity of salivary amylase is indicative of the oral cavity’s overall health, the digestive system’s efficiency, and the presence of metabolic disorders.
The assay of salivary amylase is a non-invasive, cost-effective, and reliable method for studying the physiological response to stress, nutritional imbalances, and other health-related issues.
Further research is needed to standardize the assay methodology and to explore the potential of salivary amylase activity as a biomarker for various health conditions.
This protocol will help you understand the amylase enzyme’s applications. It is an important enzyme and has a wide range of functions, like decomposing starch molecules in the human body.
This article will discuss the various applications of amylase. It is an important enzyme and has wide range of functions like decomposing starch molecules in the human body. This article will discuss the different applications of amylase.
Overall, the determination of salivary amylase activity holds promise for improving health outcomes and advancing our understanding of human physiology.
Amylase digests starch by catalyzing hydrolysis, which is splitting by the addition of a water molecule.
Discover more from Biochemistry Den
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.