The ninhydrin test is a commonly used analytical method in biochemistry, forensic science, and clinical chemistry. It is a test used to detect and identify amino acids, peptides, and proteins in a sample. This test is based on the reaction between Ninhydrin and the amino group of the amino acids present in the sample.
This article will discuss the ninhydrin test in detail, including its definition, principle, procedure, result, and uses.
Ninhydrin (2,2-Dihydroxyindane-1,3-dione) is a chemical used to detect ammonia or primary and secondary amines. When reacting with these free amines, a deep blue or purple color known as Ruhemann’s purple is produced. Ninhydrin is most commonly used to detect fingerprints, as the terminal amines or lysine residues in peptides and proteins sloughed off in fingerprints react with ninhydrin.
| Chemical Formula of Ninhydrin | C9H6O4 |
| IUPAC Name | 2,2-dihydroxyindane-1,3-dione (or) 1,2,3-Indantrione hydrate |
| Synonyms | NINHYDRIN, 485-47-2, Ninhydrine, 1,2,3-Indantrione monohydrate, Ninhydrin hydrate |
| Molecular weight of Ninhydrin | 178.14 g/mol |
| Melting point | 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) (decomposes) |
| Description | Ninhydrin appears as white to light yellow crystals or powder. Becomes anhydrous with reddening at 257-266 °F. |
Principle of Ninhydrin Test
The principle of the ninhydrin test is based on the reaction between Ninhydrin and the amino group of the amino acids present in the sample. The reaction between Ninhydrin and the amino group results in the formation of a coloured complex. The intensity of the color is directly proportional to the number of amino acids present in the sample.
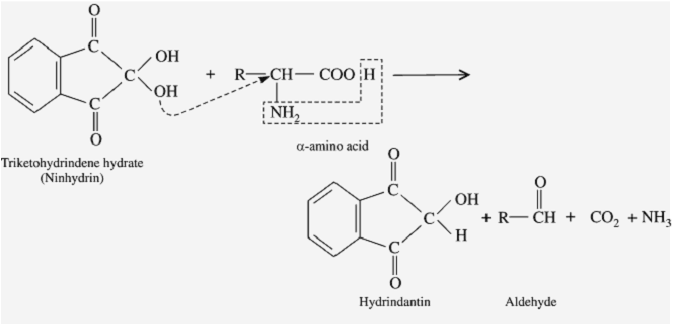
When ninhydrin reacts with amino acids, the reaction also releases CO2. The carbon in this CO2 originates from the carboxyl carbon of the amino acid. This reaction has been used to release the carboxyl carbons of bone collagen from ancient bones for stable isotope analysis in order to help reconstruct the palaeodiet of cave bears.
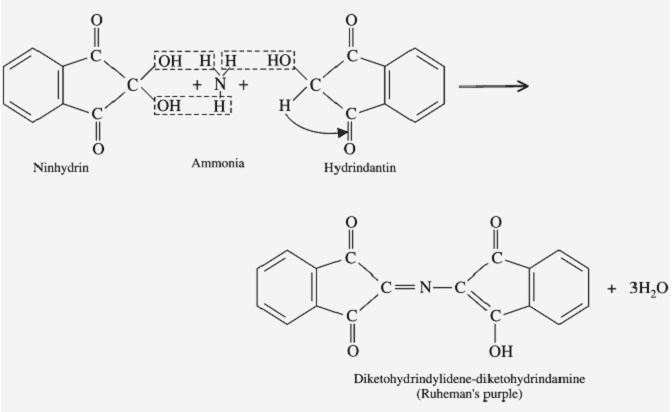
The carbon atom of a carbonyl bears a partial positive charge enhanced by neighboring electron withdrawing groups like carbonyl itself. So the central carbon of a 1,2,3-tricarbonyl compound is much more electrophilic than one in a simple ketone. Thus indane-1,2,3-trione reacts readily with nucleophiles, including water. Whereas for most carbonyl compounds, a carbonyl form is more stable than a product of water addition (hydrate), ninhydrin forms a stable hydrate of the central carbon because of the destabilizing effect of the adjacent carbonyl groups.
Procedure
The procedure for the ninhydrin test is as follows:
- Take a small amount of the sample (containing amino acids, peptides, or proteins) in a test tube.
- Add a few drops of Ninhydrin reagent to the sample. The Ninhydrin reagent is prepared by dissolving Ninhydrin in a solvent such as ethanol or acetone.
- Heat the test tube in a boiling water bath or a heating block for 10–15 minutes.
- After heating, allow the test tube to cool to room temperature.
- Observe the color of the solution. Purple or blue indicate the presence of amino acids in the sample.
Result
The result of the ninhydrin test is based on the colour of the solution after heating. The purple or blue color indicates the presence of amino acids in the sample. The intensity of the color is directly proportional to the amount of amino acids present in the sample.
Uses
The ninhydrin test has several uses in biochemistry, forensic science, and clinical chemistry. Some of the uses are as follows:
- Amino acid analysis: The ninhydrin test detects and identifies amino acids in a sample.
- Protein analysis: The ninhydrin Test detects and identifies proteins in a sample.
- Forensic science: The Ninhydrin Test detects and identifies latent fingerprints in forensic science. A ninhydrin solution is commonly used by forensic investigators in the analysis of latent fingerprints on porous surfaces such as paper. Amino acid containing fingermarks, formed by minute sweat secretions which gather on the finger’s unique ridges, are treated with the ninhydrin solution which turns the amino acid finger ridge patterns purple and therefore visible.
- Clinical chemistry: The ninhydrin test detects and identifies amino acids in biological fluids such as urine and blood.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Ninhydrin?
Ninhydrin is a chemical reagent that is used in the Ninhydrin Test. It is a powerful oxidizing agent that reacts with the amino groups of the amino acids present in the sample.
What is the principle of the ninhydrin test?
The principle of the ninhydrin test is based on the reaction between Ninhydrin and the amino group of the amino acids present in the sample.
What is the color of the solution after the ninhydrin test?
The color of the solution after the ninhydrin test is purple or blue, indicating the presence of amino acids in the sample.
Conclusion
The ninhydrin test is a simple and widely used analytical method used to detect and identify amino acids, peptides, and proteins. It is based on the reaction between ninhydrin and the amino group of the amino acids present in the sample.
The ninhydrin test has several uses in biochemistry, forensic science, and clinical chemistry. It is a valuable tool in amino acid analysis, protein analysis, forensic investigation, and clinical diagnosis.
In conclusion, the ninhydrin test is essential for researchers, scientists, and investigators in various fields. It is a simple, inexpensive, and reliable method for detecting and identifying amino acids, peptides, and proteins.
Understanding the principle and procedure of the ninhydrin test is crucial for obtaining accurate results.
Discover more from Biochemistry Den
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.


